Coatings play an essential role in maintaining the integrity of precision metal parts produced via photochemical etching, protecting parts and components from corrosion, wear, and environmental hazards. Finishing, plating, coating, or painting metal parts also serves an aesthetic and antibiotic purpose. We are well-versed in choosing the proper coating to ensure your part performs as needed.
Selecting the appropriate coating materials and methods is pivotal in achieving high-quality, finely detailed components. Engineers choose the appropriate finish based on several factors, from compatibility in final usage to environmental conditions.
It is essential to match the properties of the finish to the material properties to ensure compatibility and durability
Product specifications determine the thickness of finishes to make sure the part performs as designed
The part’s final use often determines its finish material, whether it needs corrosion protection, biocompatibility, or cosmetic treatments
Finishes must meet strict regulatory requirements, especially in medical, aerospace, defense, and technology applications
Choose coatings that match the expected lifespan of the component to reduce waste
Many coatings are available to maintain the performance of a part when exposed to harsh chemicals or corrosive substances
Environmentally friendly finishes and coatings minimize the harm to ecosystems
Low-VOC coatings reduce air politician and indoor air quality issues
Use coatings with renewable or recycled materials when possible
A wide variety of finishes and coatings are available to enhance the performance, appearance, and durability of any part. Here are some of the common coatings we apply at PEI.
Applying a platinum finish to bipolar electrolyzer plates to improve corrosion resistance, reduce the electrical contact resistance between the plate and other components, enhance the catalytic performance at the electrode-electrolyte interface, and increase the durability of every plate.
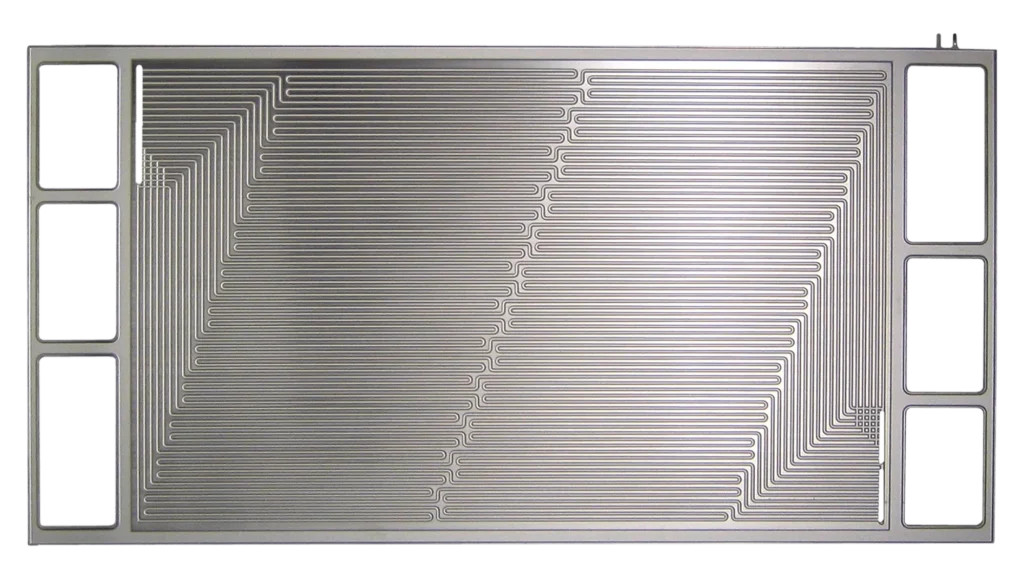
A chemical conversion coating applied during the photochemical etching process primarily used on ferrous metals like steel and stainless steel. This coating enhances corrosion and rust resistance and provides a black or dark gray appearance. Aerospace, defense, industrial, and automotive manufacturers call for this coating.
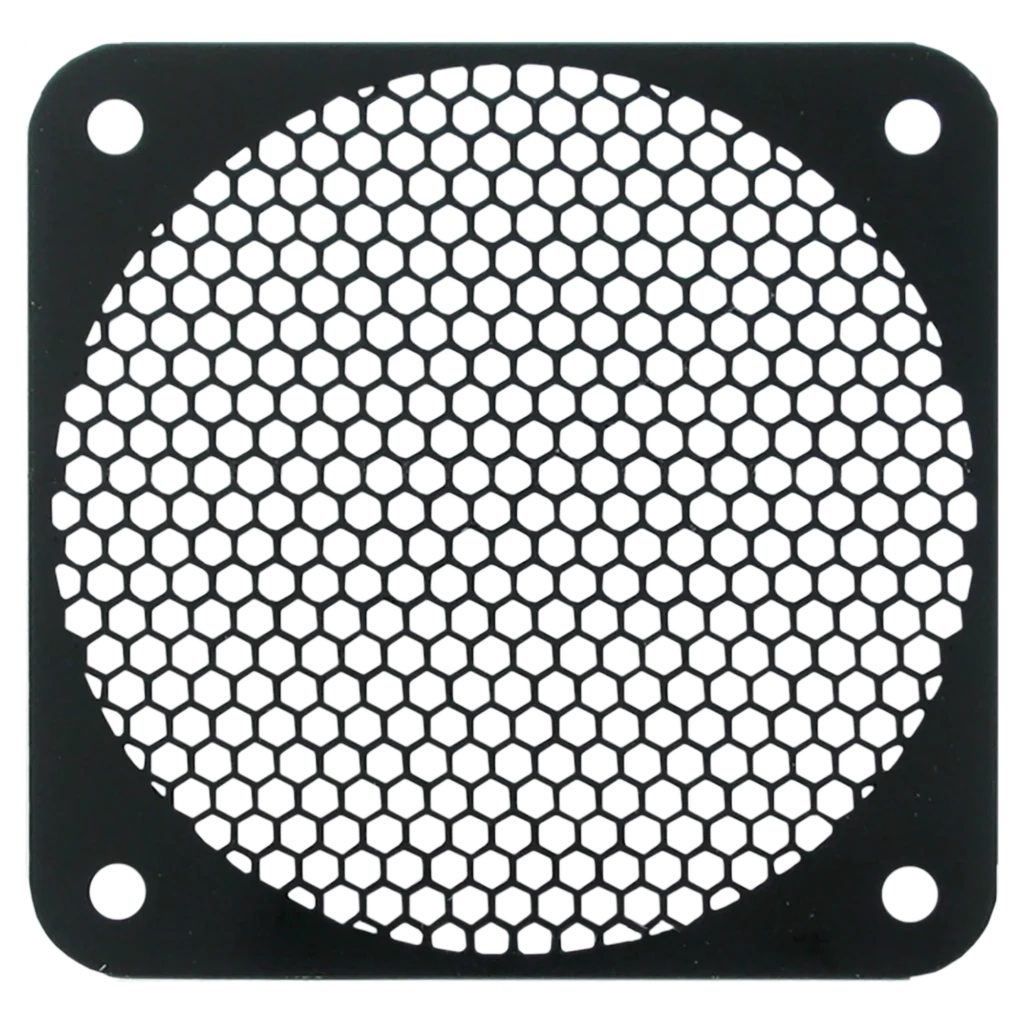
An electrochemical process where a thin layer of copper is deposited onto the surface of another metal or substrate to enhance electrical conductivity, improve corrosion resistance, and provide an attractive copper appearance. Copper plating is found on electrical connectors, printed circuit boards (PCBs), decorative items, and components in the electronics and telecommunications industries. Copper plating is frequently used as an intermediate layer before applying additional plating or finishing processes, such as tin, nickel, or chrome plating, to achieve the desired performance and aesthetics.
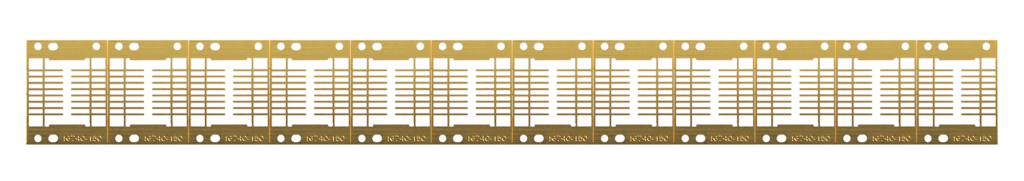
A thin layer of gold is electrochemically deposited onto the surface of a metal part or component. Gold plating enhances electrical conductivity and provides corrosion resistance. Gold plating is popular in industries such as electronics and aerospace.
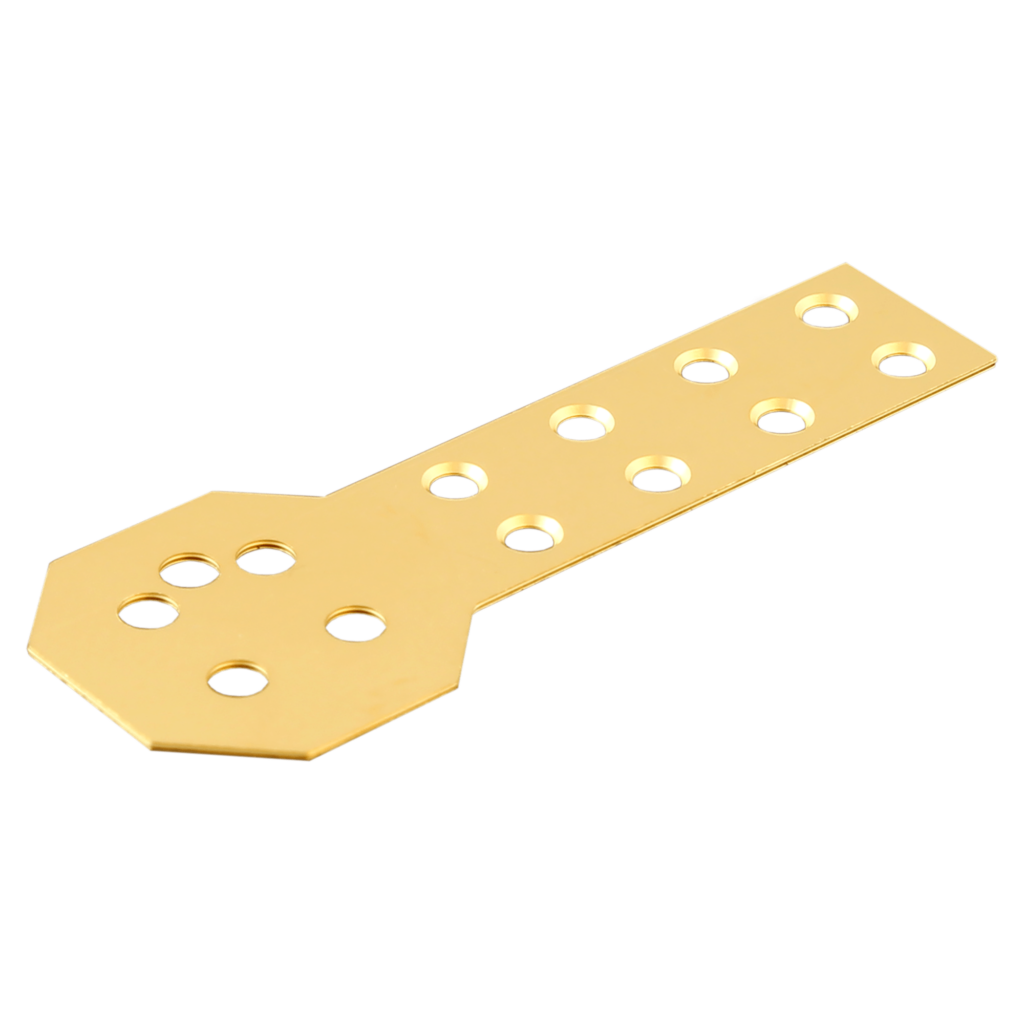
An electrochemical process where a thin layer of nickel is deposited onto the surface of a substrate, often made of metal. Nickel plating helps with corrosion and wear resistance, providing a barrier against oxidation and strengthening the substrate. Automotive parts, plumbing fixtures, electronics components, and industrial machinery, where both protection against corrosion and an attractive finish are essential, feature nickel plating. It can also serve as a base layer for subsequent coatings, such as chrome plating, to enhance performance and appearance.

A widely used finishing technique that enhances the appearance of a part or component, protects surfaces from environmental factors like corrosion and UV radiation, and provides insulation or fire resistance. Different types of paint, such as water-based, oil-based, or specialty coatings, are chosen based on the specific application requirements.
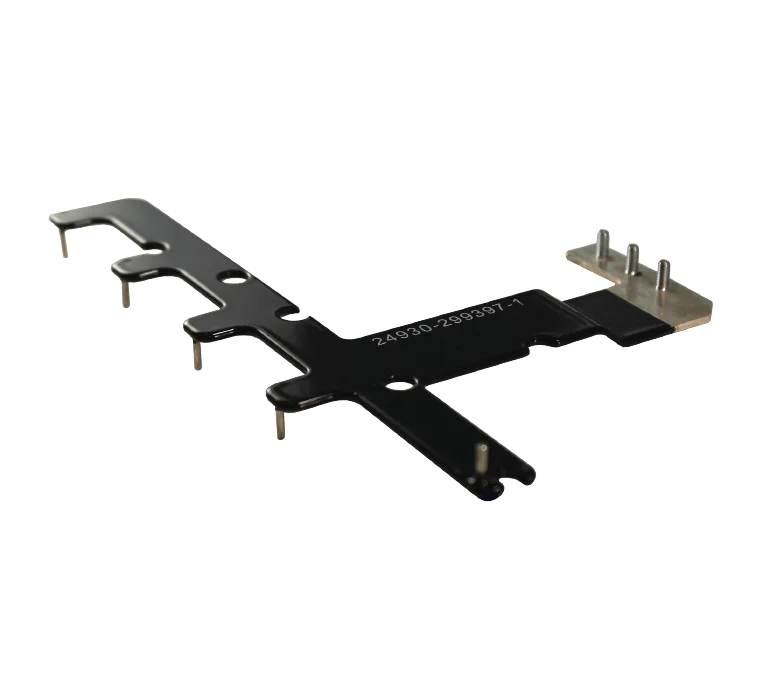

A dry finishing process used to apply a durable and protective layer to the surface of various objects. Powder coating offers numerous advantages, including excellent resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and UV radiation, a wide range of color options, and a more environmentally friendly process than traditional liquid coatings. Aerospace, defense, medical, industrial, and automotive industries use this finish.
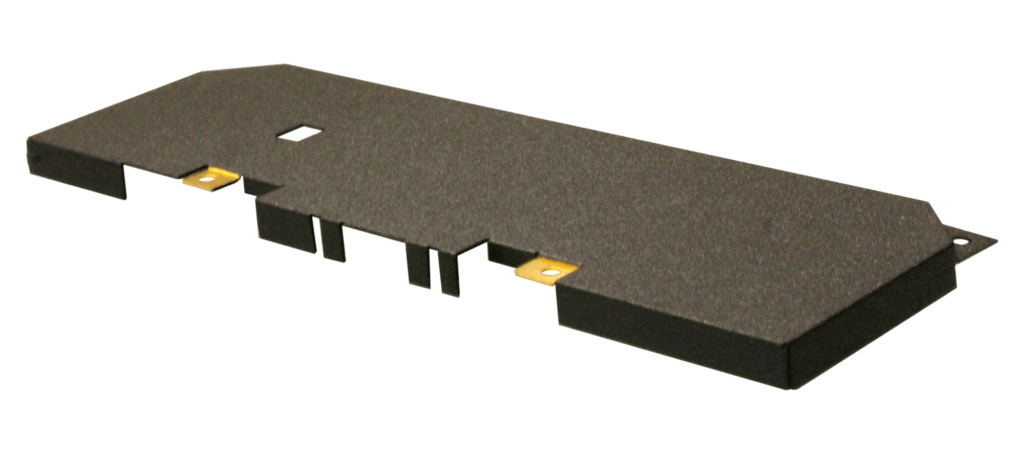
An electrochemical process that involves depositing a thin layer of silver onto the surface of a substrate, often another metal. Silver plating improves electrical conductivity and provides corrosion resistance. Due to its excellent electrical conductivity, electronics, and telecommunications manufacturers call for silver plating for connectors and conductive components. Silver’s natural antimicrobial properties also make it suitable for healthcare applications, such as coating medical instruments and equipment.
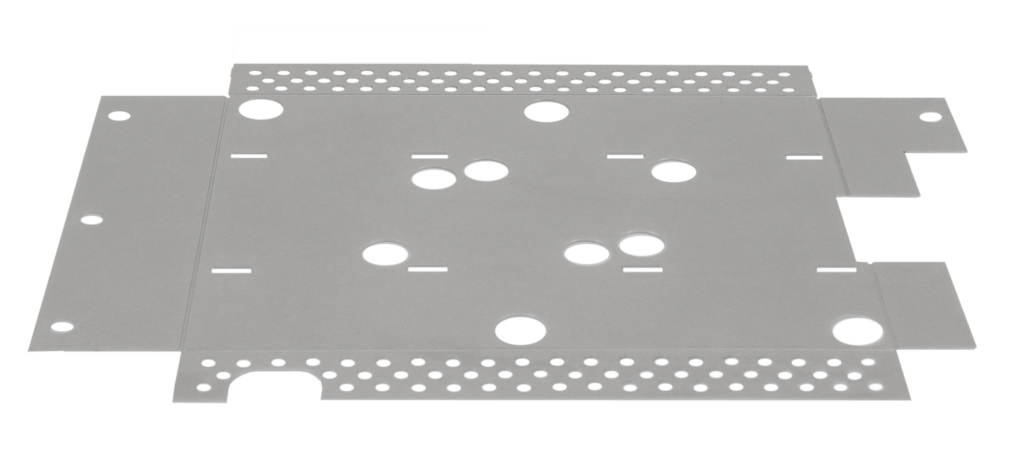
An electrochemical process that involves depositing a thin layer of tin onto the surface of a substrate, which is often made of a different metal, such as copper or steel. Its benefits include corrosion resistance and solderability, which is necessary in the electronics industry, where it’s essential to create reliable solder joints. Typical applications of tin plating include electrical connectors, printed circuit boards (PCBs), food and beverage containers (tin cans), and various consumer products. Tin plating protects metals from corrosion, particularly in harsh environments.
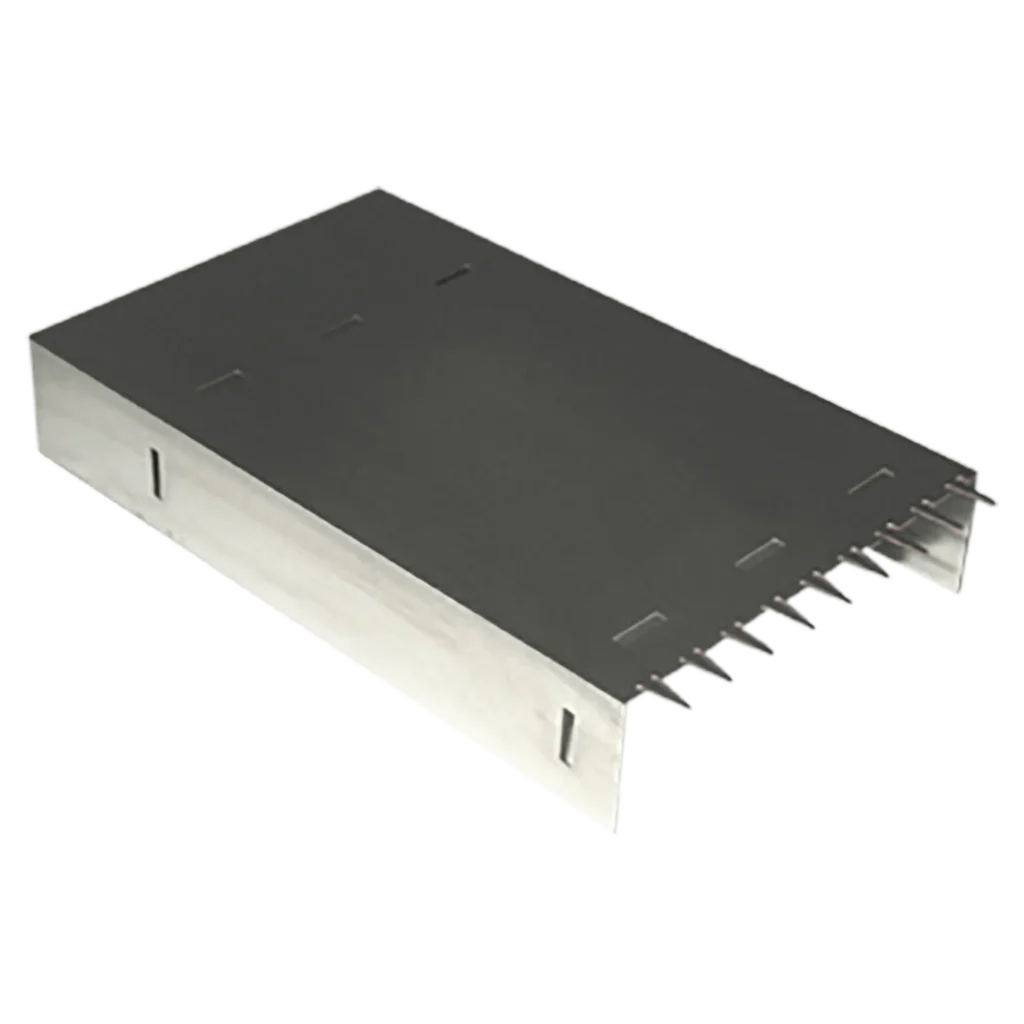
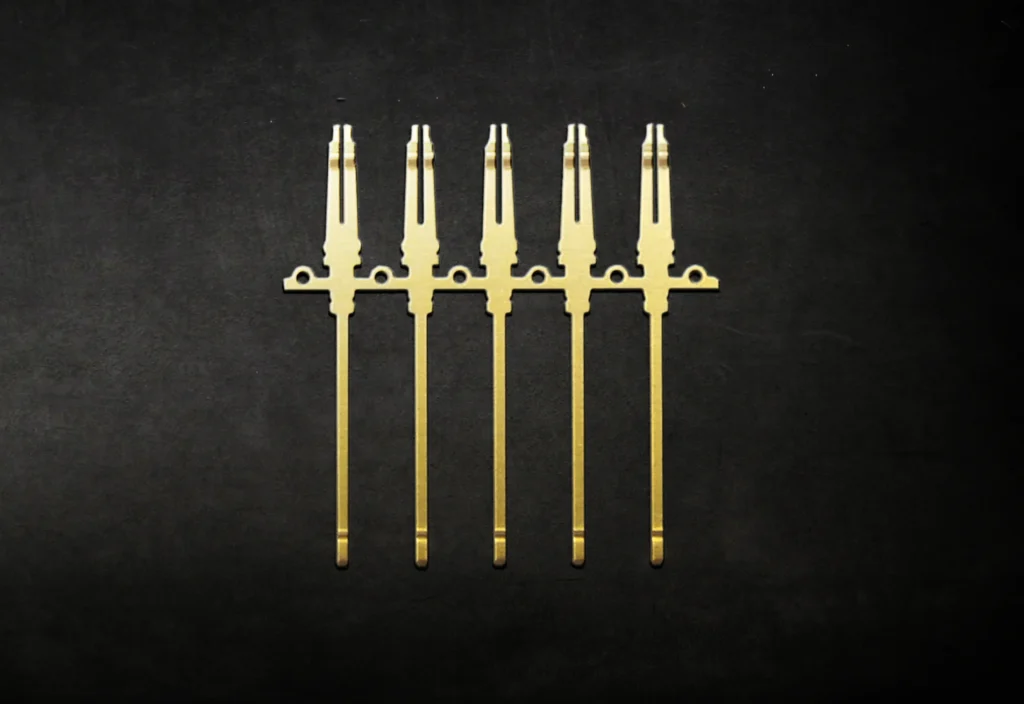
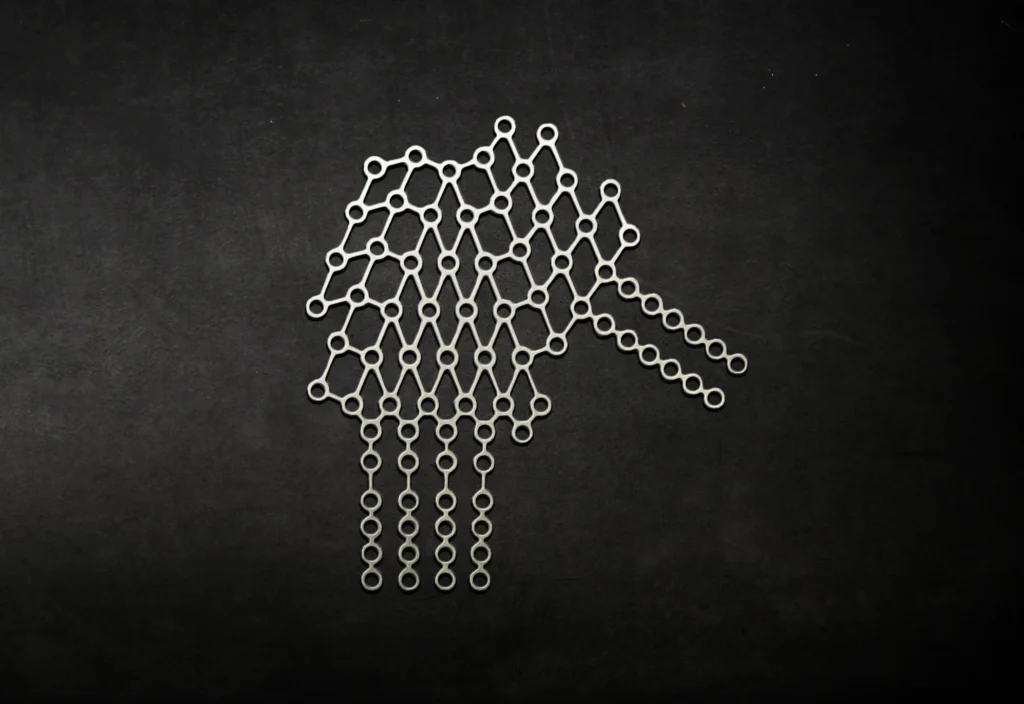



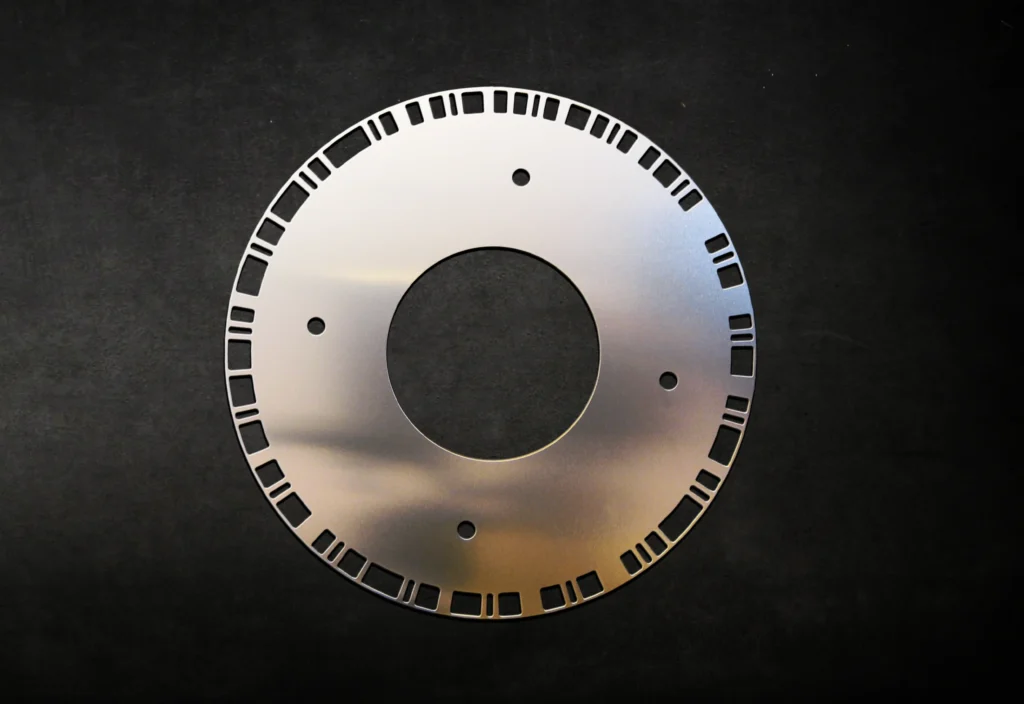
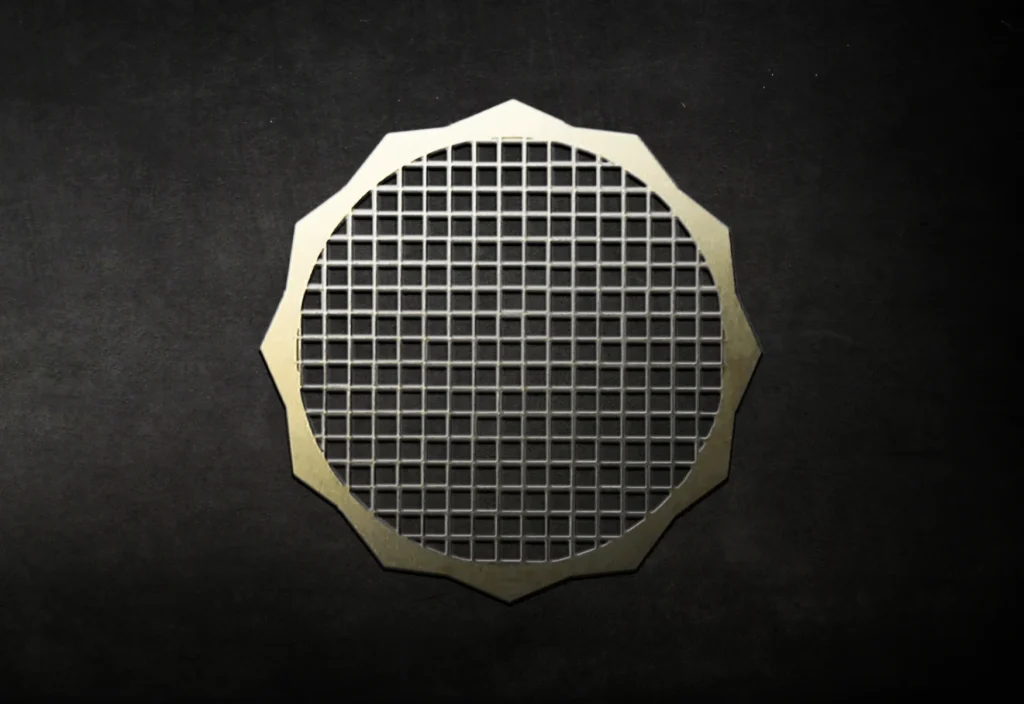


Most of the precise metal parts and components fabricated are coated in some way, whether it’s to improve electrical conductivity, appearance, or corrosion resistance. Here are a few examples:

We work with our partners to introduce new ideas and enhanced manufacturing solutions. Our engineers leverage the power of technology and decades of experience to ensure each design and plan will deliver the expected results, whether for the latest in renewable energy or a new life-saving medical technology.

PEI’s commitment to delivering thin metal parts and components utilizing precision photochemical etching dates back decades. We are the world’s leading etcher of titanium and can handle aluminum, beryllium copper, molybdenum, and many other metals. PCE is an ideal manufacturing process for rapid prototyping and high-production runs.
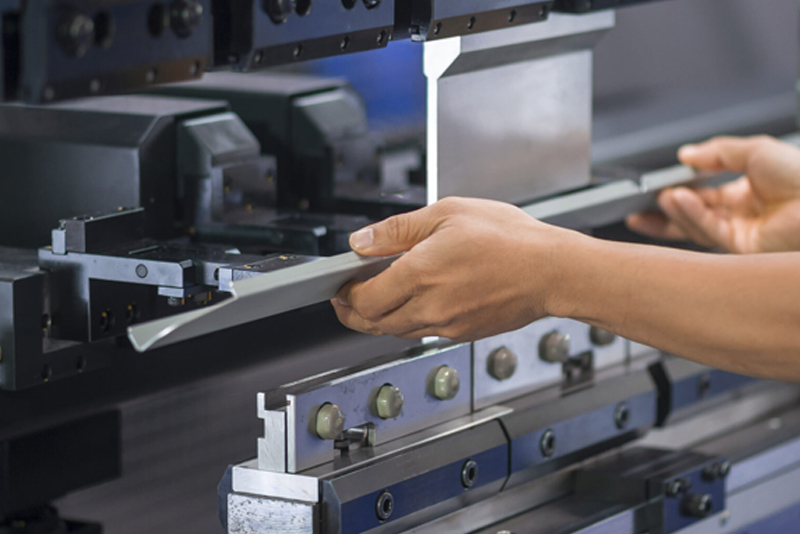

Our precision operators turn thin metal parts into reliable components with meticulous machine and manual forming techniques. PEI’s forming expertise starts at the first step, enabling us to develop highly accurate parts that our team forms to exact standards and specifications.
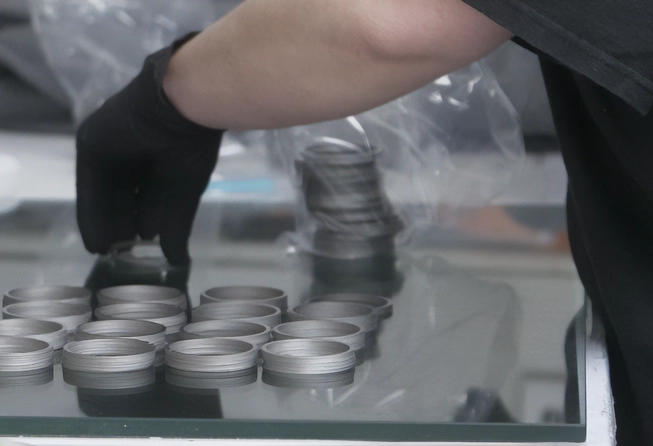

PEI delivers durable and reliable assembled components found in power-generating, life-saving, and high-technology applications worldwide. Our expert team of engineers and operators team to ensure our partners receive ready-to-implement solutions that will last.
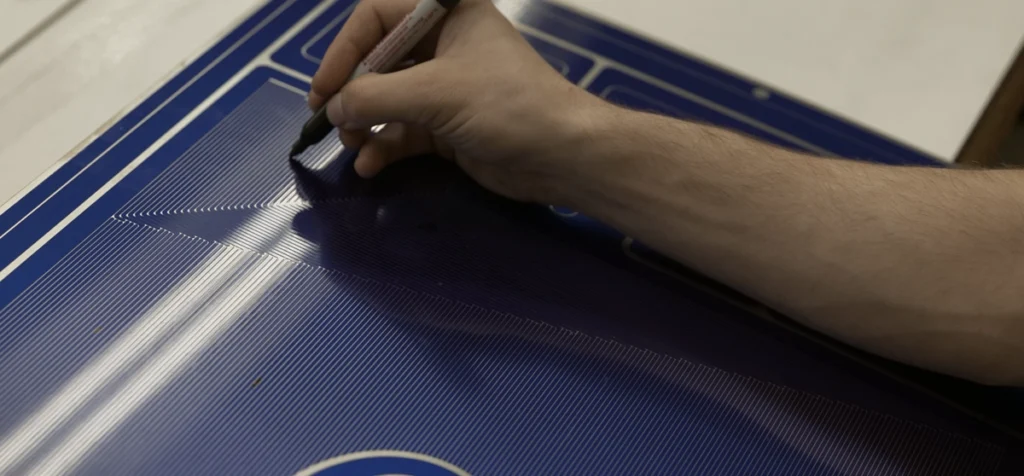

The PEI Quality Assurance team analyzes every thin metal part and component to ensure its precision, accuracy, and durability. Our team uses a combination of technological and manual inspection techniques to check for imperfections before any part or component leaves our facility.
Industries and technologies evolve when people work together to push boundaries and uncover new solutions. For over 50 years, we’ve stood shoulder to shoulder as leading companies across every market sector push forward with revolutionary changes that change the world. We are ready to share and leverage knowledge and expertise to collaborate with our customers for mutual success.




PEI’s long history of meeting and exceeding industry standards and customer expectations began in 1968. For over 50 years, we’ve kept quality assurance at the forefront of our work by training our manufacturing teams, maintaining our equipment, and establishing rigorous internal controls. PEI holds several certifications, including ISO9001:2015, AS9100:2016, and ITAR. We adhere to MIL-STD-45662, MIL-STD-105, and ANSI/ASQC Z1.4 quality standards.