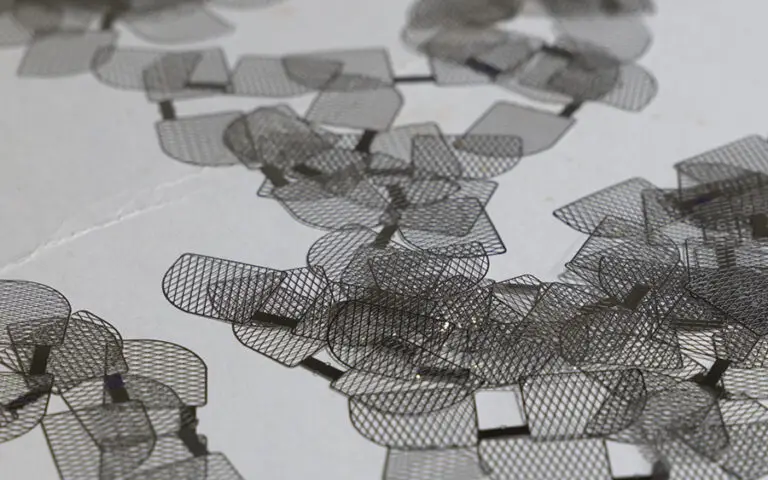
As the world shifts towards greener technologies, electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as key drivers in reducing global carbon emissions. As the demand for EVs continues to surge, manufacturers face increasing pressure to produce components that meet strict performance, safety, and sustainability standards.
With precision paramount, more and more manufacturers are leveraging photochemical etching to produce the lightweight, high-precision metal components essential for safe and efficient electric vehicles. From battery systems to intricate sensors, photochemical etching enables the production of intricate designs and maintains tight tolerances — crucial factors for the high performance and safety standards required in modern EVs.
Photofabrication Engineering, Inc. (PEI) is a leading electric vehicle parts manufacturer renowned for producing high-precision automotive metal components for electric vehicles right across the globe. Boasting extensive experience and the latest cutting-edge technology, our unique manufacturing capabilities allow us to etch metals to multiple depths without the failures common to this etching process.
In this article, we examine the key role photochemical etching plays in EV parts manufacturing, its material advantages and flexibility, and the main automotive components produced by this innovative process.

What is Precision Chemical Machining?
Photochemical etching, also known as precision chemical machining and chemical milling, is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses a light-sensitive material and chemical etching to produce intricate metal parts. This non-contact method allows for precise, clean edges without introducing stress or deformation to the material.
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, photochemical etching can handle extremely thin metals while maintaining tight tolerances. This makes it an ideal process for producing complex components that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through machining or stamping.
Some of the main advantages photochemical etching offers over other manufacturing methods include:
- High Precision and Intricacy: Photochemical etching allows for the creation of complex and detailed designs with very tight tolerances, which are difficult to achieve with traditional methods like stamping or machining.
- No Material Stress or Deformation: Since it is a non-contact process, photochemical etching doesn’t introduce mechanical stress, distortion, or burrs, preserving the integrity of thin and delicate metal parts.
- Cost-Effective Tooling: The tooling used in photochemical etching is inexpensive compared to traditional stamping or CNC machining tools. It involves creating photomasks, which are quicker and cheaper to produce.
- Flexibility with Thin Materials: This method is particularly effective for working with very thin metal sheets, which are often challenging to process using other techniques without causing deformation or breakage.
- Quick Prototyping and Modifications: The photomasks used in etching can be quickly adjusted or modified, enabling rapid prototyping and shorter lead times without the need for costly retooling.
- Material Versatility: Photochemical etching can be applied to a wide variety of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper alloys, and even titanium, making it highly adaptable to different material needs.
- No Heat-Affected Zones: Unlike processes like laser cutting, photochemical etching does not generate heat that can affect the metal’s properties or cause unwanted thermal distortion.
- Low Environmental Impact: The process is efficient and generates minimal waste, making it more environmentally friendly than some other manufacturing techniques.
- Scalability: Once the design and photomask are finalized, photochemical etching can easily scale to large-volume production while maintaining consistency and precision.
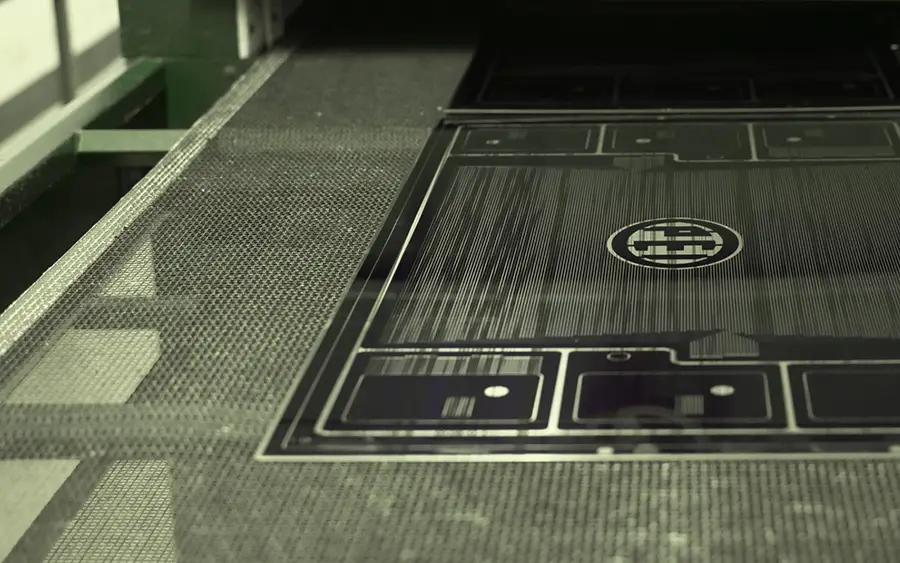
The Role of Etching in EV Parts Manufacturing
When it comes to manufacturing precise metal parts for use in electric vehicles, photochemical etching is the preferred process due to its ability to produce intricate designs and maintain tight tolerances — crucial factors for the high performance and safety standards required in EVs.
The innovative photochemical etching process delivers highly detailed, high-quality automobile parts that function efficiently and perform reliably, even in the most demanding environments.
Photochemical etching’s versatility makes it essential in producing a wide range of critical EV components, such as battery current collectors, busbars, and heat shields. Its capacity for high repeatability also allows for mass production at scale, ensuring consistency across thousands of car parts.
PEI has emerged as a key player in delivering precision components for the car manufacturing industry, ensuring that EV makers can consistently meet the rigorous demands of the market.
Material Advantages and Flexibility
The trusted team at PEI boasts extensive experience and expertise working with a wide range of high-strength steel and other metals critical to electric vehicles. EV manufacturers often require specialized materials to meet the demands of different components, such as strength, conductivity, and lightweight properties, especially for auto parts like body panels and structural components.
PEI’s photochemical etching process works with a variety of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, high-strength steel, and copper alloys — all of which are fundamental in the construction of electric vehicles. Aluminum and copper are commonly used for battery current collectors due to their conductivity and lightweight properties. Stainless and high-strength steel, on the other hand, are often used for components requiring durability, corrosion resistance, and structural integrity.
Our proven ability to etch titanium, a material commonly used in high-performance applications like battery frames and lightweight structural components, sets PEI apart from the competition. Titanium offers a unique combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for EVs that require high-strength, low-weight materials for both functional and structural auto parts.
Automotive Components Produced by Precision Chemical Machining
Photochemical etching is widely used in automotive applications to manufacture critical EV components such as battery current collectors, busbars, and heat shields. This process allows for the production of various auto parts with intricate designs and tight tolerances, including cooling plates and EMI/RFI shielding, which are essential for various applications in electric vehicles, from thermal management to electrical connectivity.
Some of the critical EV components photochemical etching is used to manufacture include:
Battery Current Collectors
These thin, lightweight plates conduct electricity within the EV battery and are typically made from copper or aluminum.
Busbars
These conductive metal strips distribute power across the electrical system, ensuring efficient energy flow.
Heat Shields
Heat shields are thin metal shields that protect sensitive components from the heat generated by the battery or motor.
Battery Management Systems
Battery management systems (BMS) monitor and control the performance, safety, and efficiency of the vehicle’s battery pack.
EMI/RFI Shielding Components
These intricate metal parts prevent electromagnetic and radio frequency interference, which is crucial for the proper functioning of vehicle electronics.
Cooling Plates
Cooling plates are etched with intricate channels that manage battery system temperatures, preventing overheating and ensuring longevity.
Sensor Components
Sensor components are small precision metal parts that detect temperature, pressure, and position throughout the vehicle.
Fuel Cell Plates
Etched bipolar plates are critical for the efficient operation of the fuel cells in hydrogen-powered EVs.
Connector Pins and Terminals
These small, intricate parts are essential for secure electrical connections throughout the EV.

Sustainability and Efficiency
As the automotive industry pushes towards sustainability, photochemical etching aligns perfectly with these goals. The process is highly efficient, producing minimal waste due to the precise removal of material. It also consumes less energy compared to other traditional metal manufacturing techniques, reducing the carbon footprint of production.
PEI is strongly committed to environmental sustainability. As a company, we take significant measures to ensure waste management practices are efficient and compliant with the highest environmental standards. By implementing eco-friendly technologies and adhering to strict regulations, we minimize our impact on the environment while delivering high-quality parts for the automotive industry.
Shaping the Future of the Electric Vehicle Industry
With its precision, versatility, and environmental benefits, photochemical etching is set to become an even more critical technology in the manufacturing of electric vehicle components, shaping the future of this rapidly evolving industry. As a leading supplier for the automotive industry, PEI’s advanced expertise in photochemical etching makes it the perfect partner for delivering high-performance, reliable components that meet the industry’s stringent demands.
PEI has been a pioneering force in leveraging photochemical etching (PCE) to enhance design flexibility for a wide range of EV components. Since 1968, we’ve continually pushed the boundaries of innovation, transforming intricate design concepts into precision-engineered metal parts with superior accuracy and efficiency.
If you’re looking to bring your most intricate and complex designs to life with precision and efficiency, PEI can help. Boasting superior design flexibility through our photochemical etching process, our team of skilled engineers and technicians works closely with clients to understand their unique design requirements and bring their vision to life.
From prototyping to high-volume production, our PCE services provide a level of versatility and reliability you simply won’t find anywhere else.
Get in touch with us today or request a quote.